1. Introduction
Since 1971 untill 2014, 38 papers about plastic surgery of the labia minora, were published [1]. First case report was made by Martincik and Malinovsky from Czech in 1971 and treated about surgical treatment of the hypertrophy of the labia minora [2]. Doctors performed posterior wedge resection. During all these years many surgeons performed a lot of similar or different techniques, but the most popular one was edge resection (direct excision). These two methods, however, have one defect - all nerves and blood vessels are cut, so sensitivity of new edge of the labia can be worse then before the procedure. In this way of thinking, Choi and Kim described a new method - deepithelialization, which preserves neurovascular supply to the edge of the labia [3]. Next step in the way of labia reduction evolution was made by Ostrzenski, who described in 2014 a fenestration labiaplasty technique with inferior flap transposition [4]. Thanks to this technique we obtain reduction in two dimensions of the labia minora - height and length. Except symmetry, natural colour and contour of the labia are preserved, and posterior edge of the fossa navicularis (labial frenulum) is restored or created “de novo”.
In 2013 reconstructive and plastic gynaecology in Poland became famous and its popularity is still growing. Despite that there are no standards or recommendations for this kind of procedures in Poland, doctors still have been doing these operations as the American College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (ACOG) recommended in 2007. Labia minora reduction procedures can be performed to alter the size and shape for such medical indications like “labial hypertrophy or asymmetrical labial growth secondary to congenital conditions, chronic irritation or excessive androgenic hormones” [5].
Reviewing labia minora reduction techniques author found many different techniques of labia minora reduction such as partial amputation (edge resection), wedge resection with its modifications (Z-plasty, inferior resection and superior pedicle flap reconstruction), de-epithelialized and laser labiaplasty [1-4,6-12].
All described methods apply only middle or posterior part of the labia minora. Most surgeons treat labia minora and clitoral hood as two different compartments. Author performed some of those methods and established hypothesis that we should see labia minora as an anatomical structure, which begins in the upper part of the vulva (periclitoral area) and ends as frenulum. On the other hand, you should not talk about restoring labia minora shape without touching clitoral hood.
2. Material and Methods
“One cut technique” is a simultaneous reduction of labia minora and clitoral hood. 3 groups of patients (5 in each) with enlarged labia minora and clitoral hood were treated with new surgical technique. First group: 5 patients aged between 16-18 y.o., all virgins; Second group: 5 women aged between 20-25 y.o., all sexual active, and Third group: 5 patients between 50-65 y.o., all after menopause. The most common symptoms, patients were suffering from were, persistent irritation with discomfort during physical activities or associated with rubbing while wearing close-fitting underwear, riding a bicycl or horseback riding, difficulties in maintaining hygiene, dyspareunia during sexual intercourse, and very important - bad psychological condition caused by negative body image perception leading to decreased self-confidence, anxiety and a social phobia, not only female-male relations. In case of the youngest group of patients, they claimed to be ashamed of their intimate places and were sure, it was (or could be in the future) the reason to avoid sexual relations. They also reported shame when taking a shower at school with other girlsthey felt different (like they “had a penis”).
A written consent was obtained from each patient and all women authorised the author to use photo images of their genital organs for publishing in medical journals.
2.1 Technique
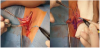
The procedures were performed under general anaesthesia because of the patients will. First and very important step was to determine the size of the labia minora to be reduced. All margins of the future incisions were determined and marked in the shape of a triangle on both sides (skin and mucus) (Figure 1a & 1b). Dissection of the skin and mucus was made with solution of 0.9% NaCl, 1% Lidocaine and 0.01% adrenaline. 30 G x 1/2 inch needle and 10 cc syringes were used. The incision was made with radio frequency device. Thanks to this surgical equipment, cut line is very straight, not too deep and damages of margins are minimal.
In fenestration part of the procedure this method is a modification of Ostrzenski technique- fenestration labiaplasty with inferior flap transposition (FLIFT) [4]. “One cut technique" involves the simultaneous excision of the mucus and skin of the labia minora (fenestration technique) and of the periclitoral skin folds, which are located on both sides along clitoral hood (Figure 2a & 2b).
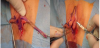
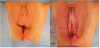
Technically, surgeon cuts skin of the labia minora in the bottom (labia minora majora fold) from the top of the clitoris towards frenulum. Second cut line goes from the top of clitoral hood along clitoris (about 1 cm right and left below the middle line of peak margin) towards the top of labia minora and turns down to the frenulum. This skin triangle is going to be deepithelialized. Similar triangle is made on internal side of the labia minora and mucus is separated from submucosal tissue. By doing so, neurovascular system of labia minora is spared, because only skin and mucus were excised from labial corp. Next, labium is divided into two parts: superior as a new top, and inferior at the base of the labium. After creating new shape of labia minus, external and internal labia laminas are being sutured on both sites separately- first with intracutaneous, continuous stitches, second with a few single stitches. All used materials are resorbable and do not need to be removed. Very important question is to bring edges of the labia and clitoral hood together without any tension (Figure 3a & 3b). Thanks to this technique we obtain two goals: first is reduction in two dimensions of the labia minora and second one is reduction of the clitoral hood in its height and width (reduction of periclitoral skin folds). This method treats labia minora and clitoral hood as one compartment, so reduction of this part of the vulva is performed with one cut simultaneously, not separately (labia and clitoral hood), as before. By doing so the shape of the new vulva looks natural (Figure 4a & 4b).
2.2 Postoperative care
Postoperatively, pain or other discomfort was controlled with oral or transrectal pain relieving pills or suppositories. During first 7 - 10 days patients were forbidden to wear underwear and were to use antiseptic solutions after using toilet. Using bath and sexual intercourses were forbidden for 6 weeks. After 7 days from surgery patients were to use externally micronised hyaluronic acid in gel, for better healing process.
3. Results
All patients treated with “One cut technique" of labia minora reduction, confirmed enlargement and/or asymmetrical labia minora and disproportionately protuberant clitoral hood. Whole group of these women reported feelings of decreased body image perception. This feeling of beeing sexual inadequate and undesirable is connected reported problem, that these women were seeing themselves as having a penis (especially because of protuberant clitoral hood). Many of them suffered because of the symptoms: irritation during physical activities, getting worse during menses (problem with pro-per personal hygiene), and reported dyspareunia during sexual intercourses. Sometimes, the biggest complain was aesthetic dissatisfaction from the appearance of enlarged labia minora and clitoral hood, but there was no problem with physical troubles. On the other hand there were many patients suffering only because of discomfort and dyspareunia, and the look was the least serious aspect of their complains. Over 90% of operated women reported both kinds of problem aesthetical and physical. “One cut technique", as simultaneous reduction of labia minora and clitoral hood, was applied without intraoperative and long term complications. In all patients, “One cut technique" of clitoral hood and labia minora reduction reduced the height and width of clitoral hood and height and length of labia minora. Thanks to that, the symmetry was established and natural colour and contour of the labium minus was preserved. Considering results, physical and emotional symptoms, and signs have been resolved. If talking about aesthetic expectations, all patients were satisfied with surgical outcomes.
4. Discussion
Analysing existing techniques of labia minora reduction, like wedge resection, central V-plasty, W-plasty and central wedge nymphotomy with Z-plasty one can have a conclusion, that these methods leave transverse scars on longitudinal anatomical structure, which is labia minora [6,8,10]. Only Choi and Ostrzenski fenestration techniques treat labia minus as such, and scars are longitudinal as well and hidden [3,4]. But even these surgical techniques do not care about clitoral hood as one compartment with labia minus. Practitioners should look at the overgrown labia minora not only for physical symptoms like discomfort during normal, ordinary physical activities, but also, or maybe mainly, as cause of sexual dysfunction (problems with sexual intercourses) and emotional disturbances (decreased feeling of self perception). It means, that aesthetic aspects play significant role in this anatomical problem and clinical symptoms are only small part of many disturbances. Very important thing is to present the patient the best surgical technique, with the most natural post operative look, and with minimal risk of complications. She also needs to understand the technique and accept it.
Analyzing existing and the most popular surgical procedures, only Ostrzenski’s technique (FLIFT) encompasses reduction of the height and length of the labia minora, and restores or creates natural appearance of the labial frenulum [4]. One cut technique of labia minora reduction also covers reduction in two dimensions and preserves natural color and contour of the labium minus with natural appearance of the posterior edge of the fossa navicularis, as FLIFT does, but difference between these two methods is significant. Neither FLIFT, nor most of other existing surgical interventions encompass simultaneous reduction of labia minora and clitoral hood [4]. Majority of surgical techniques leave clitoral hood itself and it is very common that postoperatively it looks like small penis. Composite reduction labiaplasty, by Gress, encompasses reduction of labia minora and correction of clitoral protrusion during one procedure, but scars are located cranial or caudal and they are separated from labial ones, in One cut technique it is not [12]. In case when practitioners reduce periclitoral skin folds after labium minus reduction, they create new longitudinal scars placed on both sides of the clitoral hood or transversal, like in composite reduction labiaplasty technique [12]. “One cut technique" does not do this. There is one longitudinal scar hidden in fold between labia minus and majus, so it is invisible. Because of reduction of the overgrown clitoral hood, postoperatively this part of the vulva is covered by labia majora together with labia minora, and the new look is very natural.
The only one and the best technique for all patients does not exist. Practitioner should match the proper method to the patient. If both of labia minora are thin and not very elongated, deepithelialized reduction labiaplasty can be selected [3]. If labia minora are very thick and dark, only partial amputation (edge resection) can be proposed to the patient [1,2]. And at the end, if enlargement of labia minora is connected with protuberant of the clitoris, and patient accept original, natural colour and contour of the labia, in author’s opinion “One cut technique” is the best method to achieve the best result for the patient - on the aesthetic and physical side.
Reduction of labia minora and leaving enlarged clitoral hood leads to „penis like" shape of the clitoral region. It is unacceptable for the patients. Even if there is no protuberant clitoral hood, but oversized periclitoral skin folds are noticed, labia reduction and simultaneous clitoral hood reduction with “One cut technique" should be performed. Skin excision in this region lets “put down” the clitoris. As a result whole clitoris-labia compartment will look like one, natural part of the vulva, and after surgery clitoris won’t „look out” from the labia majora (“penis like" shape).
In this study, “One cut technique" of simultaneous reduction of labia minora and clitoral hood, surgical treatment can be performed without big complications and the method achieves pleasing results. This procedure improves both problems in the same time: physical and emotional well being.
Competing Interests
The author declare that there is no competing interests regarding the publication of this article.