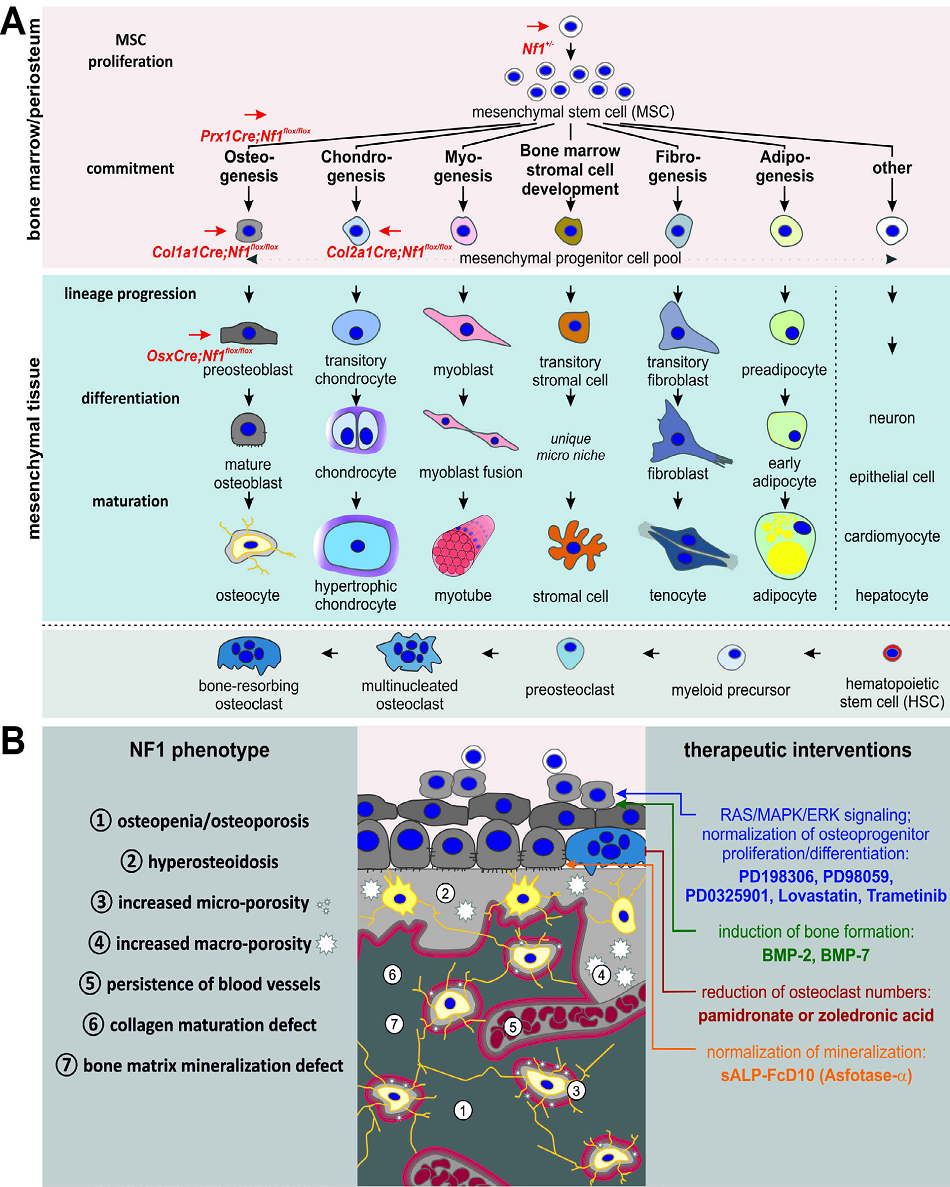
Figure 1: Scheme of mesenchymal differentiation. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) give rise to osteoblasts/osteocytes, chondrocytes, myocytes, stromal cells, tenocytes, and adipocytes. The cellular stage at which the Nf1 gene becomes inactivated in different mouse models are shown in red (Nf1+/- - heterozygous systemic knock-out, Prx1Cre;Nf1flox/flox- homozygous conditional Nf1 knock-out in mesenchymal progenitors, Col1a1Cre;Nf1flox/flox- homozygous conditional knock-out in osteoblast progenitors, Col2a1Cre;Nf1flox/flox- homozygous conditional Nf1 knock-out in chondrogenic progenitors). B Scheme of bone phenotype features upon Nf1 knock-out and therapeutic interventions. Phenotypical characteristics 1-7 of found in different NF1 mouse models are listed on the left. Pharmacological approaches tested in mouse models as well as in NF1 patients and their sites of action are shown on the right.