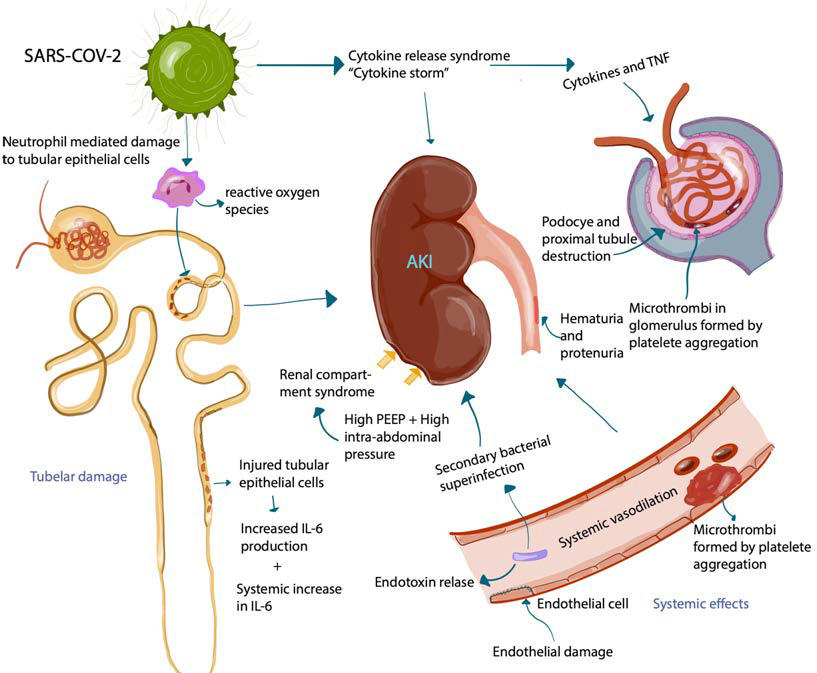
Figure 4: Proposed Pathogenesis of SARS-Cov-2 Causing Acute Kidney Injury (AKI). This is an image depicts the acute inflammatory response and systemic effects of SARS-CoV-2 on the kidneys. ACE2 receptors are found mostly on podocytes and tubular epithelial cells. Cellular internalization leads to glomerular and tubular damage. Innate and adapted immune response leads to systemic vasodilation and increased vascular permeability leading to further glomerular and tubular damage. Damage to renal tubular cells can worsen systemic inflammatory manifestations. The immune response also contributes to thrombus formation. Intragenic infections and superimposed bacterial infections are potential mediators of AKI. Intubated patients on high positive endexpiratory pressure (PEEP) settings may develop high intra-abdominal pressures potentially leading to renal compartment syndrome.