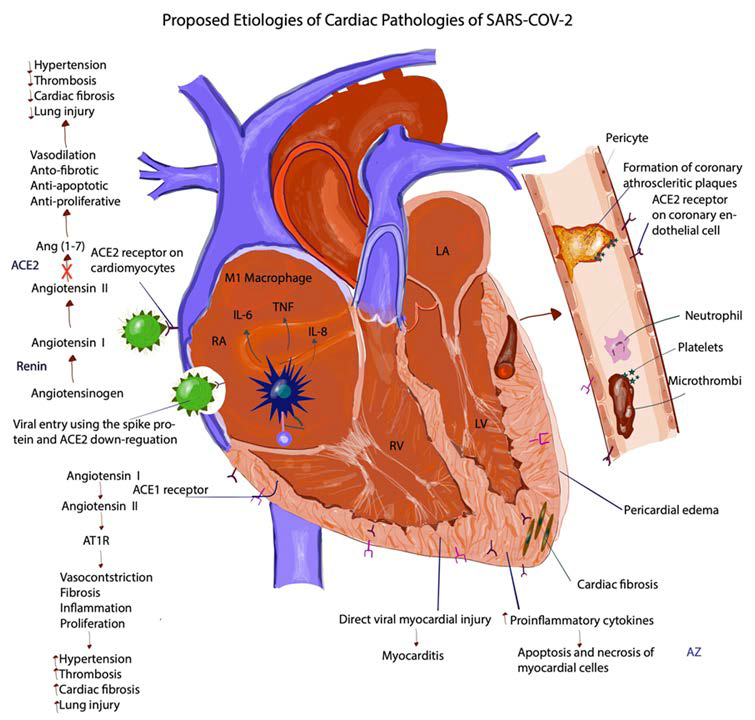
Figure 3: Proposed Etiologies of Cardiac Pathologies of SARS-CoV-2. This image describes the Renin-Angiotensin- Aldosterone (RAAS) pathway. Angiotensinogen is converted to Angiotensin I by renin, angiotensin I is converted to angiotensin 2 (Ang 2) by angiotensin converting enzyme 1 (ACE 1). ACE 2 is converted to angiotensin 1-7 (Ang 1-7) by angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE 2). Since ACE 2 is downregulated by the virus, Ang 2 is not converted to Ang 1-7 as denoted by the ‘X’ in the image. Ang 1-7 is anti-fibrotic, anti-proliferative, anti-apoptotic and vasodilatory; its downregulation leads to increased fibrosis, increased thrombosis, increased lung injury, increased blood pressure. It is postulated that direct myocardial injury by the virus can lead to myocarditis. Increase in pro-inflammatory cytokines leads to apoptosis and necrosis of myocardial cells. Increased inflammation leads to an accelerated formation of the atherosclerotic plaques and their rupture. Infiltration of the inflammatory cells in the pericardium leads to increased edema and pericarditis.