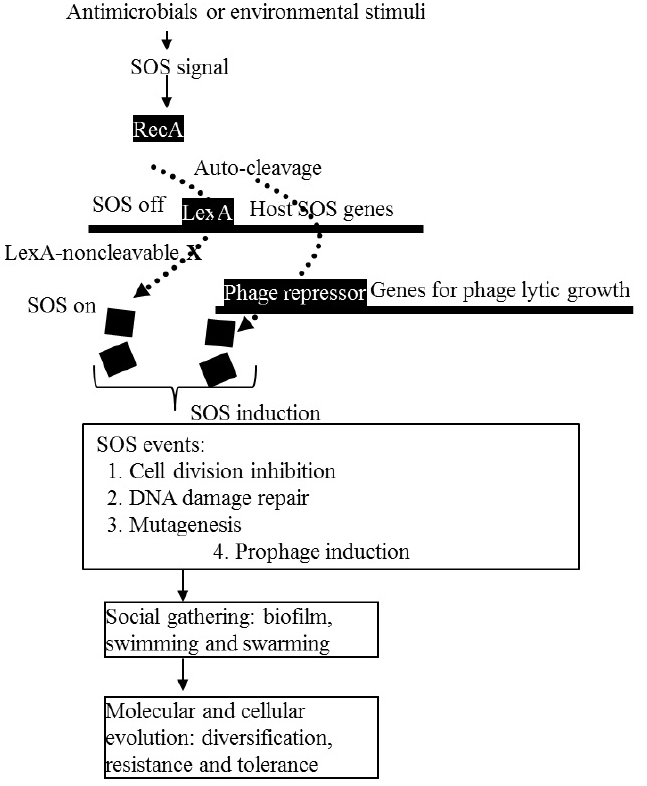
Figure 1: The SOS response in bacteria. Antibacterials or environmental stimuli, such as DNA damage antibiotics or UV, cause DNA replication stall, resulting in DNA strand breaks and singlr-strand DNAs(ssDNAs). The ssDNA are the SOS signal detected by RecA coprotease. The coprotease stimulates LexA auto-catalytic cleavage. This cleavage dismisses repression of the SOS genes to activate the SOS response. The SOS genes are thereby expressed for the repair of DNA damage. The phage repressor is also auto-cleaved, resulting in prophage induction. The repair is error-prone, thus highly mutagenic and responsible for diversification in a population.